Automatic Control Knowledge Repository
You currently have javascript disabled. Some features will be unavailable. Please consider enabling javascript.Details for: "Motion planning for closed kinematic chains using a quasistatic approach"
Name: Motion planning for closed kinematic chains using a quasistatic approach
(Key: Z7HZY)
Path: ackrep_data/problem_solutions/closed_kinematic_chains_quasistatic View on GitHub
Type: problem_solution
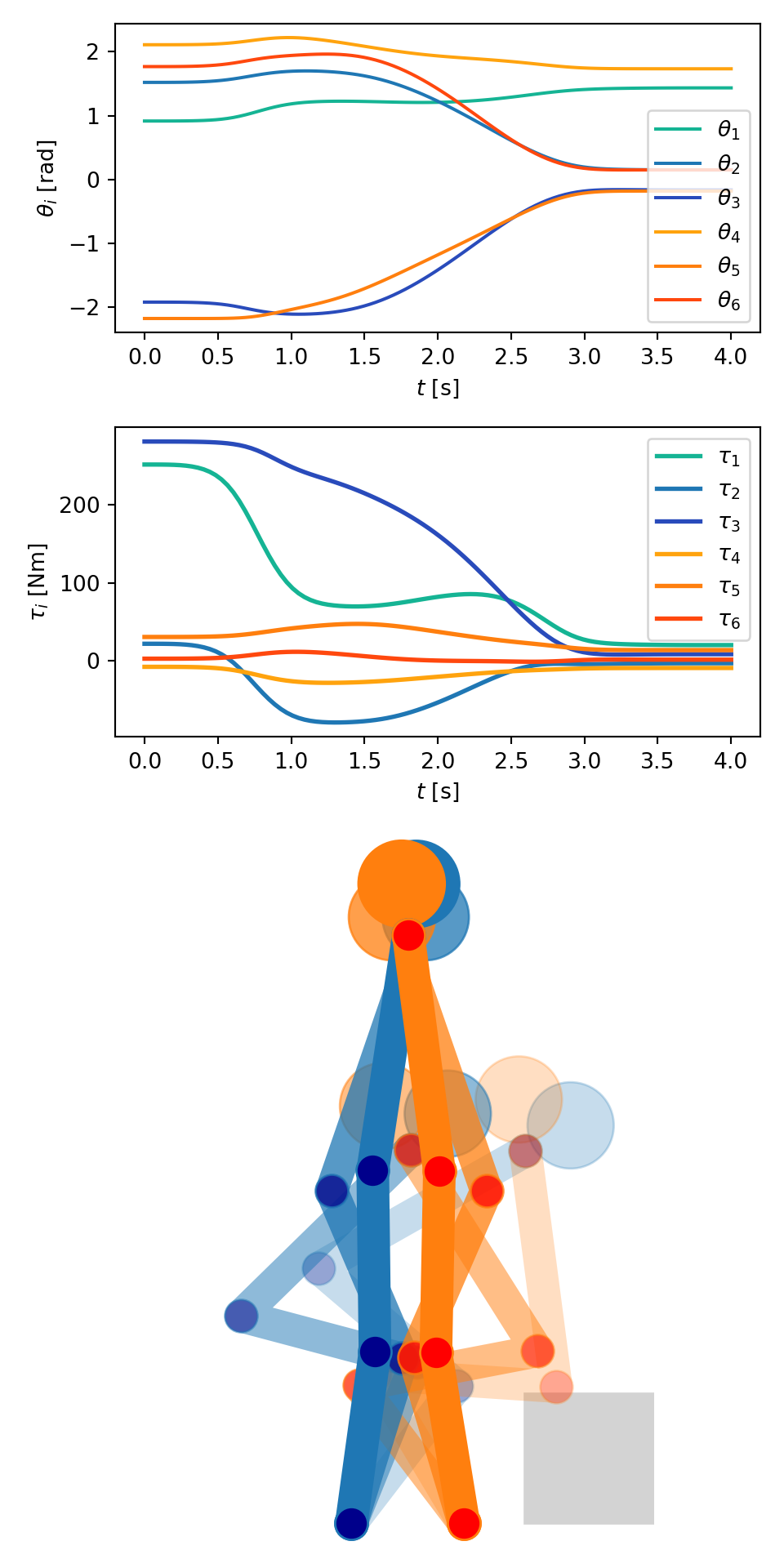
Short Description: Demonstrate motion planning for mechanical closed kinematic chains. The example used is an assisted standing up motion found in geriatric care. Created during supervision of student thesis.
Created:
Compatible Environment: default_conda_environment (Key: CDAMA)
Source Code [ / ] solution.py
Solved Problems: Motion planning for closed kinematic chains |
Used Methods:
Result: Success.
Last Build: Checkout CI Build
Runtime: 13.1 (estimated: 30s)
Plot:
The image of the latest CI job is not available. This is a fallback image.
Path: ackrep_data/problem_solutions/closed_kinematic_chains_quasistatic View on GitHub
Type: problem_solution
Short Description: Demonstrate motion planning for mechanical closed kinematic chains. The example used is an assisted standing up motion found in geriatric care. Created during supervision of student thesis.
Created:
Compatible Environment: default_conda_environment (Key: CDAMA)
Source Code [ / ] solution.py
import numpy as npy
from matplotlib import pyplot as plt, cycler
from matplotlib.gridspec import GridSpec
import symbtools as st
import symbtools.visualisation as vt
import sympy as sp
from symbtools.modeltools import Rz
import symbtools.modeltools as mt
import pickle
import os
import sys
import casadi as cs
import ipydex
from scipy.interpolate import splrep, splev, interp1d
from casadi import SX, inf
import symbtools.mpctools as mpc
from ackrep_core.system_model_management import save_plot_in_dir
class SolutionData:
pass
def solve(problem_spec):
# problem_spec is dummy
t = sp.Symbol("t") # time variable
np = 2
nq = 2
ns = 2
n = np + nq + ns
p1, p2 = pp = st.symb_vector("p1:{0}".format(np + 1))
q1, q2 = qq = st.symb_vector("q1:{0}".format(nq + 1))
s1, s2 = ss = st.symb_vector("s1:{0}".format(ns + 1))
ttheta = st.row_stack(qq[0], pp[0], ss[0], qq[1], pp[1], ss[1])
qdot1, pdot1, sdot1, qdot2, pdot2, sdot2 = tthetad = st.time_deriv(ttheta, ttheta)
tthetadd = st.time_deriv(ttheta, ttheta, order=2)
ttheta_all = st.concat_rows(ttheta, tthetad, tthetadd)
(
c1,
c2,
c3,
c4,
c5,
c6,
m1,
m2,
m3,
m4,
m5,
m6,
J1,
J2,
J3,
J4,
J5,
J6,
l1,
l2,
l3,
l4,
l5,
l6,
d,
g,
) = params = sp.symbols(
"c1, c2, c3, c4, c5, c6, m1, m2, m3, m4, m5, m6, J1, J2, J3, J4, J5, J6, l1, l2, l3, l4, l5, l6, d, g"
)
tau1, tau2, tau3, tau4, tau5, tau6 = ttau = st.symb_vector("tau1, tau2, tau3, tau4, tau5, tau6 ")
# unit vectors
ex = sp.Matrix([1, 0])
ey = sp.Matrix([0, 1])
# coordinates of centers of mass and joints
# left
G0 = 0 * ex ##:
C1 = G0 + Rz(q1) * ex * c1 ##:
G1 = G0 + Rz(q1) * ex * l1 ##:
C2 = G1 + Rz(q1 + p1) * ex * c2 ##:
G2 = G1 + Rz(q1 + p1) * ex * l2 ##:
C3 = G2 + Rz(q1 + p1 + s1) * ex * c3 ##:
G3 = G2 + Rz(q1 + p1 + s1) * ex * l3 ##:
# right
G6 = d * ex ##:
C6 = G6 + Rz(q2) * ex * c6 ##:
G5 = G6 + Rz(q2) * ex * l6 ##:
C5 = G5 + Rz(q2 + p2) * ex * c5 ##:
G4 = G5 + Rz(q2 + p2) * ex * l5 ##:
C4 = G4 + Rz(q2 + p2 + s2) * ex * c4 ##:
G3b = G4 + Rz(q2 + p2 + s2) * ex * l4 ##:
# time derivatives of centers of mass
Sd1, Sd2, Sd3, Sd4, Sd5, Sd6 = st.col_split(st.time_deriv(st.col_stack(C1, C2, C3, C4, C5, C6), ttheta))
# Kinetic Energy (note that angles are relative)
T_rot = (
(J1 * qdot1**2) / 2
+ (J2 * (qdot1 + pdot1) ** 2) / 2
+ (J3 * (qdot1 + pdot1 + sdot1) ** 2) / 2
+ (J4 * (qdot2 + pdot2 + sdot2) ** 2) / 2
+ (J5 * (qdot2 + pdot2) ** 2) / 2
+ (J6 * qdot2**2) / 2
)
T_trans = (
m1 * Sd1.T * Sd1 + m2 * Sd2.T * Sd2 + m3 * Sd3.T * Sd3 + m4 * Sd4.T * Sd4 + m5 * Sd5.T * Sd5 + m6 * Sd6.T * Sd6
) / 2
T = T_rot + T_trans[0]
# Potential Energy
V = m1 * g * C1[1] + m2 * g * C2[1] + m3 * g * C3[1] + m4 * g * C4[1] + m5 * g * C5[1] + m6 * g * C6[1]
parameter_values = list(
dict(
c1=0.4 / 2,
c2=0.42 / 2,
c3=0.55 / 2,
c4=0.55 / 2,
c5=0.42 / 2,
c6=0.4 / 2,
m1=6.0,
m2=12.0,
m3=39.6,
m4=39.6,
m5=12.0,
m6=6.0,
J1=(6 * 0.4**2) / 12,
J2=(12 * 0.42**2) / 12,
J3=(39.6 * 0.55**2) / 12,
J4=(39.6 * 0.55**2) / 12,
J5=(12 * 0.42**2) / 12,
J6=(6 * 0.4**2) / 12,
l1=0.4,
l2=0.42,
l3=0.55,
l4=0.55,
l5=0.42,
l6=0.4,
d=0.26,
g=9.81,
).items()
)
external_forces = [tau1, tau2, tau3, tau4, tau5, tau6]
dir_of_this_file = os.path.dirname(os.path.abspath(sys.modules.get(__name__).__file__))
fpath = os.path.join(dir_of_this_file, "7L-dae-2020-07-15.pcl")
if not os.path.isfile(fpath):
# if model is not present it could be regenerated
# however this might take long (approx. 20min)
mod = mt.generate_symbolic_model(T, V, ttheta, external_forces, constraints=[G3 - G3b], simplify=False)
mod.calc_state_eq(simplify=False)
mod.f_sympy = mod.f.subs(parameter_values)
mod.G_sympy = mod.g.subs(parameter_values)
with open(fpath, "wb") as pfile:
pickle.dump(mod, pfile)
else:
with open(fpath, "rb") as pfile:
mod = pickle.load(pfile)
# calculate DAE equations from symbolic model
dae = mod.calc_dae_eq(parameter_values)
dae.generate_eqns_funcs()
torso1_unit = Rz(q1 + p1 + s1) * ex
torso2_unit = Rz(q2 + p2 + s2) * ex
neck_length = 0.12
head_radius = 0.1
body_width = 15
neck_width = 15
H1 = G3 + neck_length * torso1_unit
H1r = G3 + (neck_length - head_radius) * torso1_unit
H2 = G3b + neck_length * torso2_unit
H2r = G3b + (neck_length - head_radius) * torso2_unit
vis = vt.Visualiser(ttheta, xlim=(-1.5, 1.5), ylim=(-0.2, 2))
# get default colors and set them explicitly
# this prevents color changes in onion skin plot
default_colors = plt.get_cmap("tab10")
guy1_color = default_colors(0)
guy1_joint_color = "darkblue"
guy2_color = default_colors(1)
guy2_joint_color = "red"
guy1_head_fc = guy1_color # facecolor
guy1_head_ec = guy1_head_fc # edgecolor
guy2_head_fc = guy2_color # facecolor
guy2_head_ec = guy2_head_fc # edgecolor
# guy 1 body
vis.add_linkage(
st.col_stack(G0, G1, G2, G3).subs(parameter_values),
color=guy1_color,
solid_capstyle="round",
lw=body_width,
ms=body_width,
mfc=guy1_joint_color,
)
# guy 1 neck
# vis.add_linkage(st.col_stack(G3, H1r).subs(parameter_values), color=head_color, solid_capstyle='round', lw=neck_width)
# guy 1 head
vis.add_disk(
st.col_stack(H1, H1r).subs(parameter_values), fc=guy1_head_fc, ec=guy1_head_ec, plot_radius=False, fill=True
)
# guy 2 body
vis.add_linkage(
st.col_stack(G6, G5, G4, G3b).subs(parameter_values),
color=guy2_color,
solid_capstyle="round",
lw=body_width,
ms=body_width,
mfc=guy2_joint_color,
)
# guy 2 neck
# vis.add_linkage(st.col_stack(G3b, H2r).subs(parameter_values), color=head_color, solid_capstyle='round', lw=neck_width)
# guy 2 head
vis.add_disk(
st.col_stack(H2, H2r).subs(parameter_values), fc=guy2_head_fc, ec=guy2_head_ec, plot_radius=False, fill=True
)
eq_stat = mod.eqns.subz0(tthetadd).subz0(tthetad).subs(parameter_values)
# vector for tau and lambda together
ttau_symbols = sp.Matrix(mod.uu) ##:T
mmu = st.row_stack(ttau_symbols, mod.llmd) ##:T
# linear system of equations (and convert to function w.r.t. ttheta)
K0_expr = eq_stat.subz0(mmu) ##:i
K1_expr = eq_stat.jacobian(mmu) ##:i
K0_func = st.expr_to_func(ttheta, K0_expr)
K1_func = st.expr_to_func(ttheta, K1_expr, keep_shape=True)
def get_mu_stat_for_theta(ttheta_arg, rho=10):
# weighting matrix for mu
K0 = K0_func(*ttheta_arg)
K1 = K1_func(*ttheta_arg)
return solve_qlp(K0, K1, rho)
def solve_qlp(K0, K1, rho):
R_mu = npy.diag([1, 1, 1, rho, rho, rho, 0.1, 0.1])
n1, n2 = K1.shape
# construct the equation system for least squares with linear constraints
M1 = npy.column_stack((R_mu, K1.T))
M2 = npy.column_stack((K1, npy.zeros((n1, n1))))
M_coeff = npy.row_stack((M1, M2))
M_rhs = npy.concatenate((npy.zeros(n2), -K0))
mmu_stat = npy.linalg.solve(M_coeff, M_rhs)[:n2]
return mmu_stat
ttheta_start = npy.r_[0.9, 1.5, -1.9, 2.1, -2.175799453493845, 1.7471971159642905]
mmu_start = get_mu_stat_for_theta(ttheta_start)
connection_point_func = st.expr_to_func(ttheta, G3.subs(parameter_values))
cs_ttau = mpc.casidify(mod.uu, mod.uu)[0]
cs_llmd = mpc.casidify(mod.llmd, mod.llmd)[0]
controls_sp = mmu
controls_cs = cs.vertcat(cs_ttau, cs_llmd)
coords_cs, _ = mpc.casidify(ttheta, ttheta)
# parameters: 0: value of y_connection, 1: x_connection_last,
# 2: y_connection_last, 3: delta_r_max, 4: rho (penalty factor for 2nd persons torques),
# 5:11: ttheta_old[6], 11:17: ttheta:old2
#
P = SX.sym("P", 5 + 12)
rho = P[10]
# weightning of inputs
R = mpc.SX_diag_matrix((1, 1, 1, rho, rho, rho, 0.1, 0.1))
# Construction of Constraints
g1 = [] # constraints vector (system dynamics)
g2 = [] # inequality-constraints
closed_chain_constraint, _ = mpc.casidify(mod.dae.constraints, ttheta, cs_vars=coords_cs)
connection_position, _ = mpc.casidify(list(G3.subs(parameter_values)), ttheta, cs_vars=coords_cs) ##:i
connection_y_value, _ = mpc.casidify([G3[1].subs(parameter_values)], ttheta, cs_vars=coords_cs) ##:i
stationary_eqns, _, _ = mpc.casidify(eq_stat, ttheta, controls_sp, cs_vars=(coords_cs, controls_cs)) ##:i
g1.extend(mpc.unpack(stationary_eqns))
g1.extend(mpc.unpack(closed_chain_constraint))
# force the connecting joint to a given hight (which will be provided later)
g1.append(connection_y_value - P[0])
ng1 = len(g1)
# squared distance from the last reference should be smaller than P[3] (delta_r_max):
# this will be a restriction between -inf and 0
r = connection_position - P[1:3]
g2.append(r.T @ r - P[3])
# change of angles should be smaller than a given bound (P[5:11] are the old coords)
coords_old = P[5:11]
coords_old2 = P[11:17]
pseudo_vel = (coords_cs - coords_old) / 1
pseudo_acc = (coords_cs - 2 * coords_old + coords_old2) / 1
g2.extend(mpc.unpack(pseudo_vel))
g2.extend(mpc.unpack(pseudo_acc))
g_all = mpc.seq_to_SX_matrix(g1 + g2)
### Construction of objective Function
obj = controls_cs.T @ R @ controls_cs + 1e5 * pseudo_acc.T @ pseudo_acc + 0.3e6 * pseudo_vel.T @ pseudo_vel
OPT_variables = cs.vertcat(coords_cs, controls_cs)
# for debugging
g_all_cs_func = cs.Function("g_all_cs_func", (OPT_variables, P), (g_all,))
nlp_prob = dict(f=obj, x=OPT_variables, g=g_all, p=P)
ipopt_settings = dict(max_iter=5000, print_level=0, acceptable_tol=1e-8, acceptable_obj_change_tol=1e-6)
opts = dict(print_time=False, ipopt=ipopt_settings)
xx_guess = npy.r_[ttheta_start, mmu_start]
# note: g1 contains the equality constraints (system dynamics) (lower bound = upper bound)
delta_phi = 0.05
d_delta_phi = 0.02
eps = 1e-9
lbg = npy.r_[[-eps] * ng1 + [-inf] + [-delta_phi] * n, [-d_delta_phi] * n]
ubg = npy.r_[[eps] * ng1 + [0] + [delta_phi] * n, [d_delta_phi] * n]
# ubx = [inf]*OPT_variables.shape[0]##:
# lower and upper bounds for decision variables:
# lbx = [-inf, -inf, -inf, -inf, -inf, -inf, -inf, -inf]*N1 + [tau1_min, tau4_min, -inf, -inf]*N
# ubx = [inf, inf, inf, inf, inf, inf, inf, inf]*N1 + [tau1_max, tau4_max, inf, inf]*N
rho = 3
P_init = npy.r_[
connection_point_func(*ttheta_start)[1],
connection_point_func(*ttheta_start),
0.01,
rho,
ttheta_start,
ttheta_start,
]
args = dict(
lbx=-inf,
ubx=inf,
lbg=lbg,
ubg=ubg, # unconstrained optimization
p=P_init, # initial and final state
x0=xx_guess, # initial guess
)
solver = cs.nlpsol("solver", "ipopt", nlp_prob, opts)
sol = solver(**args)
global_vars = ipydex.Container(old_sol=xx_guess, old_sol2=xx_guess)
def get_optimal_equilibrium(y_value, rho=3):
ttheta_old = global_vars.old_sol[:n]
ttheta_old2 = global_vars.old_sol2[:n]
opt_prob_params = npy.r_[y_value, connection_point_func(*ttheta_old), 0.01, rho, ttheta_old, ttheta_old2]
args.update(dict(p=opt_prob_params, x0=global_vars.old_sol))
sol = solver(**args)
stats = solver.stats()
if not stats["success"]:
raise ValueError(stats["return_status"])
XX = sol["x"].full().squeeze()
# save the last two results
global_vars.old_sol2 = global_vars.old_sol
global_vars.old_sol = XX
return XX
y_start = connection_point_func(*ttheta_start)[1]
N = 100
y_end = 1.36
y_func = st.expr_to_func(t, st.condition_poly(t, (0, y_start, 0, 0), (1, y_end, 0, 0)))
def get_qs_trajectory(rho):
pseudo_time = npy.linspace(0, 1, N)
yy_connection = y_func(pseudo_time)
# reset the initial guess
global_vars.old_sol = xx_guess
global_vars.old_sol2 = xx_guess
XX_list = []
for i, y_value in enumerate(yy_connection):
# print(i, y_value)
XX_list.append(get_optimal_equilibrium(y_value, rho=rho))
XX = npy.array(XX_list)
return XX
rho = 30
XX = get_qs_trajectory(rho=rho)
def smooth_time_scaling(Tend, N, phase_fraction=0.5):
"""
:param Tend:
:param N:
:param phase_fraction: fraction of Tend for smooth initial and end phase
"""
T0 = 0
T1 = Tend * phase_fraction
y0 = 0
y1 = 1
# for initial phase
poly1 = st.condition_poly(t, (T0, y0, 0, 0), (T1, y1, 0, 0))
# for end phase
poly2 = poly1.subs(t, Tend - t)
# there should be a phase in the middle with constant slope
deriv_transition = st.piece_wise(
(y0, t < T0), (poly1, t < T1), (y1, t < Tend - T1), (poly2, t < Tend), (y0, True)
)
scaling = sp.integrate(deriv_transition, (t, T0, Tend))
time_transition = sp.integrate(deriv_transition * N / scaling, t)
# deriv_transition_func = st.expr_to_func(t, full_transition)
time_transition_func = st.expr_to_func(t, time_transition)
deriv_func = st.expr_to_func(t, deriv_transition * N / scaling)
deriv_func2 = st.expr_to_func(t, deriv_transition.diff(t) * N / scaling)
C = ipydex.Container(fetch_locals=True)
return C
N = XX.shape[0]
Tend = 4
res = smooth_time_scaling(Tend, N)
def get_derivatives(XX, time_scaling, res=100):
"""
:param XX: Nxm array
:param time_scaling: container for time scaling
:param res: time resolution of the returned arrays
"""
N = XX.shape[0]
Tend = time_scaling.Tend
assert npy.isclose(time_scaling.time_transition_func([0, Tend])[-1], N)
tt = npy.linspace(time_scaling.T0, time_scaling.Tend, res)
NN = npy.arange(N)
# high_resolution version of index arry
NN2 = npy.linspace(0, N, res, endpoint=False)
# time-scaled verion of index-array
NN3 = time_scaling.time_transition_func(tt)
NN3d = time_scaling.deriv_func(tt)
NN3dd = time_scaling.deriv_func2(tt)
XX_num, XXd_num, XXdd_num = [], [], []
# iterate over every column
for col in XX.T:
spl = splrep(NN, col)
# function value and derivatives
XX_num.append(splev(NN3, spl))
XXd_num.append(splev(NN3, spl, der=1))
XXdd_num.append(splev(NN3, spl, der=2))
XX_num = npy.array(XX_num).T
XXd_num = npy.array(XXd_num).T
XXdd_num = npy.array(XXdd_num).T
NN3d_bc = npy.broadcast_to(NN3d, XX_num.T.shape).T
NN3dd_bc = npy.broadcast_to(NN3dd, XX_num.T.shape).T
XXd_n = XXd_num * NN3d_bc
# apply chain rule
XXdd_n = XXdd_num * NN3d_bc**2 + XXd_num * NN3dd_bc
C = ipydex.Container(fetch_locals=True)
return C
C = XX_derivs = get_derivatives(XX[:, :], time_scaling=res)
expr = mod.eqns.subz0(mod.uu, mod.llmd).subs(parameter_values)
dynterm_func = st.expr_to_func(ttheta_all, expr)
def get_torques(dyn_term_func, XX_derivs, static1=False, static2=False):
ttheta_num_all = npy.c_[XX_derivs.XX_num[:, :n], XX_derivs.XXd_n[:, :n], XX_derivs.XXdd_n[:, :n]] ##:S
if static1:
# set velocities to 0
ttheta_num_all[:, n : 2 * n] = 0
if static2:
# set accelerations to 0
ttheta_num_all[:, 2 * n :] = 0
res = dynterm_func(*ttheta_num_all.T)
return res
lhs_static = get_torques(dynterm_func, XX_derivs, static1=True, static2=True) ##:i
lhs_dynamic = get_torques(dynterm_func, XX_derivs, static2=False) ##:i
mmu_stat_list = []
for L_k_stat, L_k_dyn, ttheta_k in zip(lhs_static, lhs_dynamic, XX_derivs.XX_num[:, :n]):
K1_k = K1_func(*ttheta_k)
mmu_stat_k = solve_qlp(L_k_stat, K1_k, rho)
mmu_stat_list.append(mmu_stat_k)
mmu_stat_all = npy.array(mmu_stat_list)
solution_data = SolutionData()
solution_data.tt = XX_derivs.tt
solution_data.xx = XX_derivs.XX_num
solution_data.mmu = mmu_stat_all
solution_data.vis = vis
save_plot(problem_spec, solution_data)
return solution_data
def save_plot(problem_spec, solution_data):
color_cycle = cycler(color=["#15B494", "#1F77B4", "#294BBB", "#FFA30E", "#ff7f0e", "#FF480E"])
fig = plt.figure(figsize=(5, 10))
grid = GridSpec(4, 1)
plt.subplot(grid[0, 0])
plt.gca().set_prop_cycle(color_cycle)
plt.plot(solution_data.tt, solution_data.xx[:, :6], "-")
plt.xlabel(r"$t$ [s]")
plt.ylabel(r"$\theta_i$ [rad]")
plt.legend(
["$\\theta_1$", "$\\theta_2$", "$\\theta_3$", "$\\theta_4$", "$\\theta_5$", "$\\theta_6$"], loc="lower right"
)
plt.subplot(grid[1, 0])
plt.gca().set_prop_cycle(color_cycle)
plt.plot(solution_data.tt, solution_data.mmu[:, :6], "-", lw=2)
plt.xlabel(r"$t$ [s]")
plt.ylabel(r"$\tau_i$ [Nm]")
plt.legend(["$\\tau_1$", "$\\tau_2$", "$\\tau_3$", "$\\tau_4$", "$\\tau_5$", "$\\tau_6$"])
frames = [0, 25, 60, 99]
ttheta_onion = solution_data.xx[:, :6]
ttheta_onion = ttheta_onion[frames, :]
_, ax = solution_data.vis.create_default_axes(fig=fig, add_subplot_args=grid[2:, 0])
ax.grid(False)
ax.set_axis_off()
ax.set_xlim(-0.3, 0.7)
ax.set_ylim(-0.05, 1.6)
# draw chair
from matplotlib.patches import Rectangle
chair = Rectangle((0.4, 0), 1, 0.3, color="lightgray")
ax.add_patch(chair)
# plot onion skins
# change_alpha=True tweaks the alpha channel, change_alpha=False tweaks the color lightness
solution_data.vis.plot_onion_skinned(ttheta_onion, axes=ax, change_alpha=True, max_lightness=0.75)
plt.tight_layout()
save_plot_in_dir()
Solved Problems: Motion planning for closed kinematic chains |
Used Methods:
Result: Success.
Last Build: Checkout CI Build
Runtime: 13.1 (estimated: 30s)
Plot:

The image of the latest CI job is not available. This is a fallback image.